What is Skin Pigmentation?

Skin pigmentation means colouring of the skin. It relies on specialised cells called melanocytes that produce melanin. Melanin gives colour to the skin, hair, and iris of the eyes. Individuals with low levels of it have a light complexion tone and the ones with high amounts have a darker complexion.
Pigmentation as a medical condition is usually spots or patches that appear on the skin. It could be small patches, bigger ones or it might affect your entire body. Overtime and left unchecked, it can affect the colour of the skin and then results in uneven skin complexion.
Types of Pigmentation
The common types of pigmentation are as follows:
Hyperpigmentation

It refers to the areas of the skin that are darker than the surrounding region. It is one of the most usual skin conditions that affects the individuals of all skin types. Hyperpigmentation types cover:
| Type |
Description |
Symptoms |
Areas affected on the body |
Individuals affected |
| Melasma |
Caused due to hormonal changes, pregnancy, or exposure to the sun. |
Dark brown patches |
Commonly on hands, face, stomach, neck and shoulders |
Pregnant, pre or post-menopausal women |
| Solar lentigines (sun spots) |
Caused due to excessive sun exposure |
Black or brown spots on body |
Commonly on hands, face, and arms |
Adults and older people having prolonged sun exposure |
| Freckles |
Caused due to long exposure to the sun and could be hereditary |
Small dots that are prevalent in people with fair complexion |
Seen on all parts of body |
People with any age group having lighter skin tone |
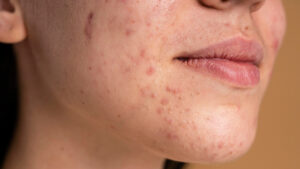
| Post- inflammatory hyperpigmentation |
Caused due to injury, burns, acne and treatments like lasers, peeling or dermabrasion |
Dark patches or spots on the skin |
Seen anywhere on the body |
People with acne-prone skin or suffered any injury to the skin |
Hypopigmentation
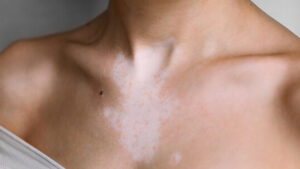
It refers to discoloration of certain areas of skin due to abrupt decrease in melanin production. It can be due to injuries or any related disease or trauma. Hypopigmentation types include:
| Type |
Description |
Symptoms |
Areas affected on the body |
Individuals affected |
| Vitiligo |
Caused when the melanin cells get damaged. |
Discoloured white patches |
Seen anywhere on the body, hair,and inside of the mouth |
Mostly begins from childhood, adults can also be affected |
| Albinism |
Caused by absence of melanin and is hereditary |
Spots on skin, changes in hair colour, or vision impairment |
Commonly seen on skin, but can affect eye and hair |
Transmitted genetically |
| Pityriasis alba |
Caused due to long exposure to the sun and is hereditary |
Dry patches on skin that are usually round or oval |
Seen on face, upper arms, chest, and neck |
Mostly affects children and young adults with genetic predisposition |
Pigmentation
Pigment producing cells known as melanocytes are present at the base of epidermis (top layer of the skin). Injury, inflammation or overexposure to sun rays can disrupt melanin production of these cells. This disturbs the base layer of epidermis and causes melanin to spill into the dermis layer. This leads to discoloration of skin and thus results in skin condition known as pigmentation.
The factors that cause pigmentation are:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Imbalance in the levels of oestrogen and progesterone in the body can trigger the production of melanin. The fluctuations can take place during pregnancy or menopause.
- Injury: Skin injuries like cuts or bruises can cause inflammatory reactions on the site causing melanin levels to increase.
- Overexposure to sun: Ultraviolet radiations of the sunlight can reach deep into the skin and cause the pigment to come to the surface.
- Blue light: Increase in screen time due to work from home (WFH) can cause hyperpigmentation. The blue light coming from laptops, mobile phones and other electronic gadgets severely harms skin and eyes.
- Genetics: Genes are responsible for the regulation of melanin production. Thus, certain pigmentation concerns may be hereditary.
How to Get Rid of Pigmentation?
While pigmentation can't be completely treated, it tends to be controlled and decreased. All types of hyperpigmentation like melasma or sun spots and hypopigmentation like vitiligo or albinism can be addressed.
Topical creams
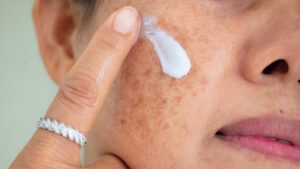
It is the primary line of skin pigmentation treatment. We should be regular in using creams or serums to see consistent results. Some of the key ingredients you should look out in products for addressing pigmentation are:
Retinoids
They are the derivatives of vitamin A. Due to their anti-ageing and skin-lightening properties, retinoids help in lessening the hyperpigmentation, appearance of wrinkles, and combat acne. It also comes in the form of serum that can be applied directly on your skin. Retinoids can also be applied in combination with a mild anti- inflammatory cream.
Niacinamide
It is vitamin B3 derivative. It decreases the hyperpigmentation by lightening dark spots and also reduces the appearance of wrinkles. Kosmoderma Acne and Blemish Control Serum contains niacinamide, turmeric, aloe vera, and ginger root extract. It is dermatologically tested and helps in boosting the production of collagen for lightening dark spots and clears scars. Aloe vera in the serum is used to moisturise and soothe the skin.
Shop Now
Glycolic acid
It is a water soluble acid and is found in toners, serums and other cosmetic products. It is used to exfoliate the skin by removing the dead skin cells from the surface. Also, it permits new skin cells to renew.
Glycolic acid is rich in antioxidants, which help to heal sun spots and other types of hyperpigmentation. It lessens dark spots caused by UV rays of sun and makes skin more radiant. As we know, excess production of melanin results in dark, dull patches, and uneven skin complexion. Glycolic acid works by inhibiting the release of melanin and likewise controls pigmentation.
Kojic acid
It is a skin lightening agent that works by preventing the formation of an enzyme that produces melanin.
Kojic acid is found in cleansers, serums and creams. It is obtained from fungus and helps in easing up scars from acne. It is a UV protectant and an expert in treating melasma by lightening the pigmented regions.
Cosmetic treatments
These treatment not only improve the appearance of skin but also help in reducing pigmentation. Some of the procedures to lessen the appearance of pigmentation include:
Chemical peels

Chemical peels are suggested for people with conditions like skin break out scars, sun harm, melasma, hyperpigmentation, scars, redness, and uneven skin tone. The method includes applying chemical solutions to the area impacted by pigmentation. It leads to exfoliation of the skin and causing it to peel off. The outcome is a smoother and more youthful looking skin. Depending on the depth of peeling, there are three types of peels:
1. Light or superficial chemical peels
It removes the outer layer of the skin. Alpha hydroxy, a mild acid, is used for exfoliation of the skin. It is used to treat acne, uneven skin tone and dryness.
2. Medium chemical peels
It removes the damaged skin cells from the outer layer of skin and from the upper part of the middle layer of skin. Glycolic acid and trichloroacetic acid are mainly used.
3. Deep chemical peels
It eliminates damaged skin cells even more deep inside the skin. Trichloroacetic acid and phenol are mainly used.
Laser therapy
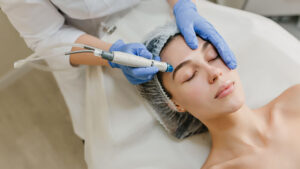
The service leverages laser beams that targets the melanin concentration on the affected region. In the heat thus generated, more obscure cells are destroyed, thus in turn lessens pigmentation. There are two types of lasers:
1. Ablative lasers
These lasers remove the outer layer of skin and invigorate the development of collagen fibres. These lasers are strong, intense and require carbon dioxide or erbium for treating pigmentation, scars, wrinkles and fine lines.
2. Non ablative lasers
These lasers use both heat and light but without affecting the upper layer of the skin. These lasers are less invasive and target the middle layer to enhance the growth of collagen.
Intense pulsed light (IPL)
It is a light therapy used for treating sun damage, freckles, spots and unwanted hair. IPL and laser have a slight difference. Unlike laser therapy, IPL involves the usage of different wavelengths of light. The light coming out of IPL is more dissipated and less engaged, and can easily enter the second layer of the skin. The pigmented cells in the skin absorb light and convert into heat to eliminate the spots, freckles or any other hyperpigmentation signs.
Microdermabrasion
It is a safe procedure to improve the skin complexion and improve the appearance of spots. In this service, an applicator with a rough surface is used to tenderly sand away the thicker external layer of the skin to reestablish or revive it.
Tips to Prevent & Reduce Pigmentation in Future
- Don't touch your face frequently: It feels enticing to scratch a mosquito bite, squeeze blackheads or pop pimples. This will only lead to inflammation and thus in turn leads to skin discolouration.
- Keep your hydrated to improve cell turnover: Staying hydrated and using moisturising agents rich in glycerin and hyaluronic acid helps in making new cells that actively brightens your skin.
- Over the counter (OTC) treatments: Products containing retinoids, kojic acid, and glycolic acid can be used on a day-to-day basis. This will help in preventing hyperpigmentation in future.
- Wear sunscreen: It is one of the most effective ways. Using a sunscreen with SPF more than 30 can block the harmful UV rays from the sun. It prevents dark spots from becoming even darker.
Conclusion
Pigmentation is a common skin condition and is often harmless. They are of different types and can be treated in numerous ways. In some cases, dark areas can fade away by applying topical creams. In other cases, chemical treatments are needed to do the same. Pigmentation and its related problems can be avoided by following a diligent skincare regime.







